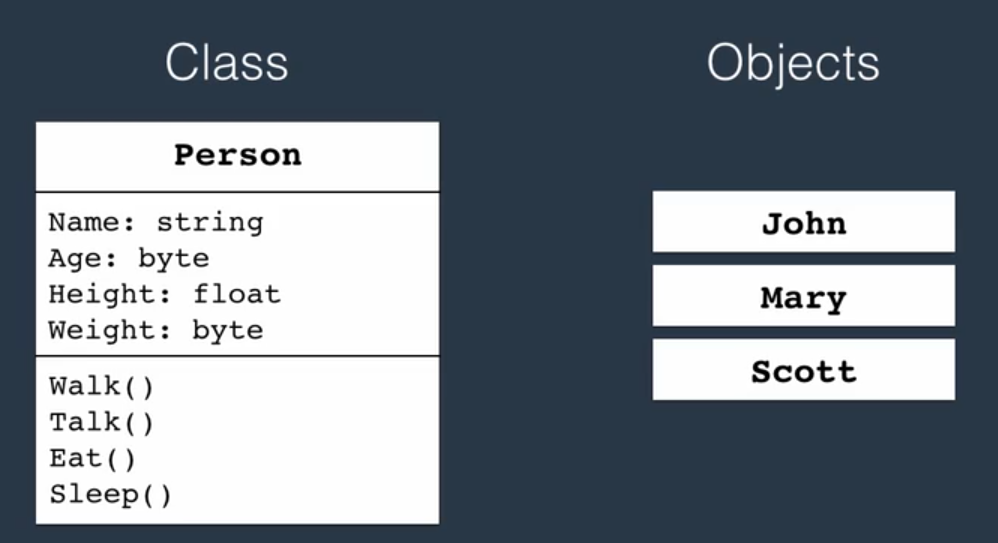
- In real life, a car is an object. The car has attributes, such as weight and color, and methods, such as drive and brake.
- A Class is like an object constructor, or a “blueprint” for creating objects.
- اعرف ان ال class عبارة عن Reference Types
- بيـ Support الـ Cs Inheritance
Create a Class and Object
- We use Pascal case to name this
- We will use Camel Case when naming parameters of methods
public class Car
{
string color = "red"; // attribute - field
static void Main() // return type -> void
{
Car myObj = new Car();
Console.WriteLine(myObj.color);
}
}- Object is an instance of a class.
- لما بتبدأ تستخدمه يبقا كدا فيه حاجة في ال memory
- We use
newto make new object We can create multiple objects of one class:
class Car
{
string color = "red";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car myObj1 = new Car();
Car myObj2 = new Car();
Console.WriteLine(myObj1.color);
Console.WriteLine(myObj2.color);
}
}
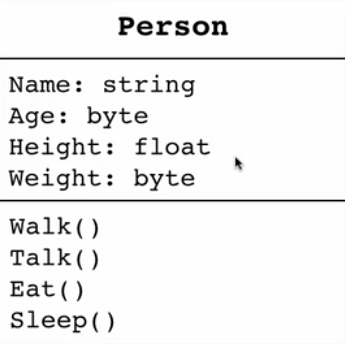
Class Members
- أي حاجة جوا ال class اقدر اقول عليها member من الكلاس
- ممكن تبقا عبارة عن field أو method
- Data (represented by fields)
- Behaviour (represented by methods/functions)
- Property
- Event
- UML: Classes
تقدر تخصص لكل واحدة منهم access modifier خاص بيها
// The class
class MyClass // Internal by deafult OR Public
{
//Class members
string color = "red"; // field or attribute
int maxSpeed = 200; // field
public void fullThrottle() //method
{
Console.WriteLine("I am the car");
}
}طبعا ممكن تخلي ال fields فاضية ومتديلهاش قيمة وتبدأ تديلها القيمة وانت بتعرف ال object
class Car
{
string model;
string color;
int year;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car Ford = new Car();
Ford.model = "Mustang";
Ford.color = "red";
Ford.year = 1969;
Car Opel = new Car();
Opel.model = "Astra";
Opel.color = "white";
Opel.year = 2005;
Console.WriteLine(Ford.model);
Console.WriteLine(Opel.model);
}
}- Note that: The method must be
publicThe reason is simple: astaticmethod can be accessed without creating an object of the class, whilepublicmethods can only be accessed by objects.
- We have two types of members:
Instance members
- بيبقا ليها علاقة بال object نفسه وكل object يقدر ينادي على ال instances الخاصة به
var corn = new Person();
corn.Introduce(); // Instance
Static Members
- تقدر توصلها من خلال ال class نفسه
- بنستخدمها في الحاجات اللي مش منطقي تبقا موجودة في أكتر من مكان زي مثلًا ال
WriteLine- انك تعرف وقت دلوقتي مش المفروض لكل object بس هو لكلاس بس
DateTime.Now - عندي console واحد وهو دا اللي ممكن أطبع من خلاله وهو كلاس
Console.WriteLine()
- انك تعرف وقت دلوقتي مش المفروض لكل object بس هو لكلاس بس
public class Person
{
public static int PeopleCount = 0; // Static
}Example
// Instance
public class Person
{
public string Name;
public void Introduce(string to)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi {0}, I am {1}", to, Name);
}
public Person Parse(string str)
{
// It makes a new person
var person = new Person();
person.Name = str;
return person;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
var p = person.Parse("corn");
p.Introduce("Pop");
}
}
// Static
public class Person
{
public string Name;
public void Introduce(string to)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi {0}, I am {1}", to, Name);
}
public static Person Parse(string str)
{
// It makes a new person
var person = new Person();
person.Name = str;
return person;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = Person.Parse("Corn");
person.Introduce("Pop");
}
}Constructor
- we talked about Cs Constructor before.
- We can make more than one constructor.
Class Types
- Concrete Class (Regular Class)
- Abstract Class: Not fully implemented
- Static Class: بنستخدم من الكلاس مباشر مش لازم أعمل أوبجيكت
- Sealed Class: لو مش عايز حاجة بعد كدا تورث مني
- Partial Class: لو أكتر من حد شغال على نفس الكلاس وحابب تقسمه على كذا فايل