What is Interfaces?
- هو عبارة عن Code contract بين الـ Developer اللي كتبه والـ Developer اللي هيعمله Implementation
- Interface → prototype - code contract - no data in
- If class follows an interface we must initialize all interface (methods, properties) in the class
- بيتكتب جوا الـ Cs Namespace وقولنا الموضوع دا في Inside Namespace
- مينفعش أعمل Object من الـ Interface بس ينفع أعمل Reference لأن أصلًا بيبقا فيه Bodies بس فهو هيعمل ايه؟
interface IMyType
{
int Salary {get; set;}
void MyFun();
void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}Practical with classes
- الـ Reference من الـ Interface يقدر يشاور على Object من الـ Class بشرط إن الـ Class يكون بي Implement الـ Interface ودي الطريقة الوحيدة اللي أقدر أوصل بيها للـ Default implemented method
- مبستخدم الـ Default implemented method غير في حالة واحدة وهي ان يبقا عندي أكتر من Class ليهم نفس الـ Interface وبيبقا عندهم Function مشتركة
- للوهلة الأولى تحس العملية دي شبه الـ Cs Binding
- بستخدمها في الأغلب لو عندي Function عامة معرفش ممكن يبقا فيها ايه وممكن تتغير زي مثال الـ Series فمثلًا
GetNextهتتغير وبيبقا زي عقد وبجبر الشخص اللي بيعمله انه يمشي على العقد دا
Why Interfaces
حلت مشكلتين عندنا:
- معنديش Multiple Cs Inheritance في الـ CSharp في الـ Cs Class
- معنديش Cs Inheritance في الـ Cs Struct
Explicitly and Implicitly
- لو عندك Class وهو بيعمل Implement لأكتر من Interface وهم فيهم Function ليها نفس الإسم في الـ Interfaces دي وانت روحت عملت Implement للـ Function دي Implicitly ساعتها الـ Compiler بيفترض ان الـ Function دي للإتنين
الفرق بين الـ Implicitly و الـ Explicitly:
- الـ Implicitly: بيعتبر الـ Function لو مشتركة نفس الـ Implementation لكله
- الـ Explicitly: لو عايز أغير الـ Implementation للفانكشن المشتركة دي لأكتر من Interface خد بالك الـ Function متنفعش تبقا Public ودايمًا بتبقا Private اللي هو الـ Default للحاجات جوا الـ Class ولو عايز أوصل للـ Function دي لازم أعمل Reference من الـ Interface دي وأشاور على Object من الكلاس اللي بيعمل Implementation له
Example
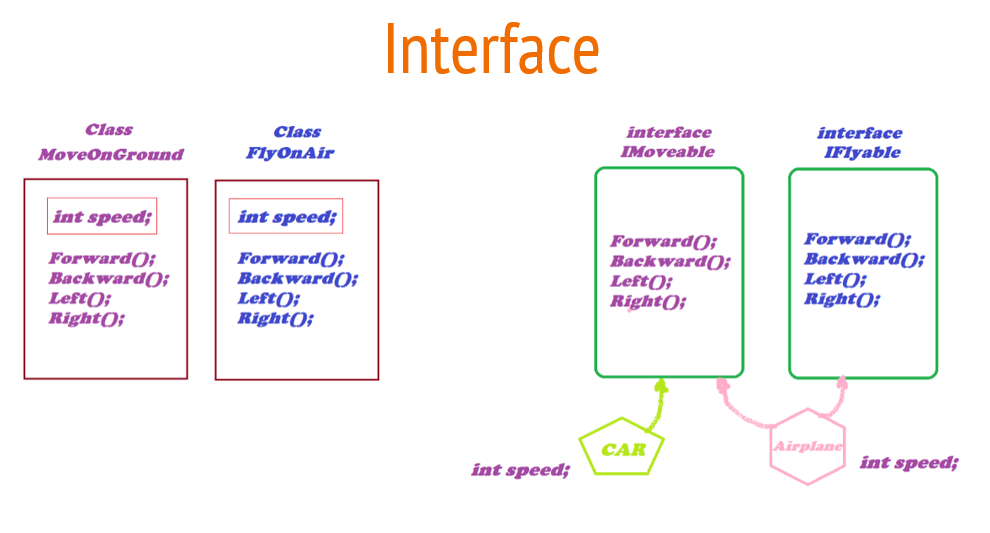
عندي اتنين Classes واحدة للعربية وواحدة للطيارة والعربية بتحرك عالأرض بس انما الطيارة بتتحرك في الطيارة وفي الجو هتلاقي ان الـ Functions بتاع الإتنين ليهم نفس الإسم فبالتالي لازم أستخدم الـ Explicitly Implement
interface IMoveable
{
void Forward();
}
internal interface IFlyable
{
void Forward();
}
class Car : IMoveable
{
public void Forward()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
class Airplane : IMoveable, IFlyable
{
//public void Forward() // implicit implementation
//{
// throw new NotImplementedException();
//}
void IMoveable.Forward() // explicit implementation
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
void IFlyable.Forward()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
// MAIN
Car c1 = new();
c1.Forward();
Airplane a1 = new();
//a1.Forward(); // Cannot call method 'Forward()' because it is Explicitly Implemented
IMoveable moveable = new Airplane();
moveable.Forward();1. Implicit Implementation:
When you implicitly implement an interface, the members of the interface are public members of the class. These members can be accessed directly via an instance of the class, and there is no need to cast the instance to the interface type.
When to use:
- If you want the interface’s members to be directly accessible via the class’s object.
public interface IAnimal
{
void Speak();
}
public class Dog : IAnimal
{
// Implicit implementation
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("Woof!");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.Speak(); // No cast required, direct access
}
}2. Explicit Implementation:
When you explicitly implement an interface, the members are not directly accessible via an instance of the class. Instead, they can only be accessed by casting the instance to the interface type. This is useful when you want to provide different implementations for the same method name across multiple interfaces or avoid exposing interface members as part of the class’s public API.
- When to use:
- If you want to hide the interface methods from being accessed directly through the class’s object.
- If there are method name conflicts when implementing multiple interfaces.
public interface IAnimal
{
void Speak();
}
public class Dog : IAnimal
{
// Explicit implementation
void IAnimal.Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("Woof!");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Dog dog = new Dog();
// dog.Speak(); // This will give a compilation error
// To call Speak, cast the object to IAnimal
((IAnimal)dog).Speak(); // Casting is required
}
}Key Differences:
- Accessibility:
- Implicit: Interface methods are accessible directly via the class instance.
- Explicit: Interface methods are only accessible via a cast to the interface type.
- Use case:
- Implicit: Suitable when you want the methods to be part of the class’s public API.
- Explicit: Suitable when you want to implement multiple interfaces with methods of the same name or when you don’t want the interface methods to be part of the public API.
Simple Example
interface IMyType
{
public int Salary { get; set; } // Signature of Property
void MyFunc();
void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}
//class MyType : IMyType
//{
// public int Salary { get => throw new NotImplementedException(); set => throw new NotImplementedException(); }
// public void MyFunc()
// {
// throw new NotImplementedException();
// }
//}
// => goes to (arrow function) for oneline functions
interface IMyType
{
public int Salary { get; set; } // Signature of Property
void MyFunc();
void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}
class MyType : IMyType
{
public int Salary { get => throw new NotImplementedException(); set => throw new NotImplementedException(); }
public void MyFunc()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
// MAIN
IMyType T; // Reference to an Interface
//IMyType T2 = new IMyType(); // ERROR -> Cannot create an object of an Interface
IMyType T3 = new MyType(); // OK -> Upcasting from class to Interface
MyType T1 = new MyType();
T1.MyFunc();
// T1.Print(); //ERROR -> Cannot call a method of an Interface from class
T3.Print(); // OK -> Down casting from Interface to classAccess modifiers
Transclude of Cs-Access-Modifiers#inside-cs-interface-interface^917dd1
Examples
Example 1
namespace InterfaceEx1
{
interface ISeries
{
int Current { get; }
void GetNext();
void Reset();
}
class FibSeries : ISeries
{
int current;
int prev;
public FibSeries()
{
prev = 0;
current = 1;
}
public int Current { get { return current; } }
public void GetNext()
{
int Temp = Current;
current += prev;
prev = Temp;
}
public void Reset()
{
current = 1;
prev = 0;
}
}
struct SeriesByTwo : ISeries
{
int current;
public int Current { get { return current; } }
public void GetNext()
{
current += 2;
}
public void Reset()
{
current = 0;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void ProcessSeries (ISeries series)
{
for ( int i=0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.Write($"{series.Current} , ");
series.GetNext();
}
Console.WriteLine("");
series.Reset();
}
static void MainV1(string[] args)
{
SeriesByTwo series01 = new SeriesByTwo();
ProcessSeries(series01);
ISeries series02; ///Valid ,
//Refrence to any Class\Struct Implementing ISeries Interface
//series01 = new ISeries(); ///Not Valid
series02 = new FibSeries();
ProcessSeries(series02);
}
}
}Example 2
namespace D04
{
interface IMyType
{
//int X; Not Supported
void FunOne();
decimal Salary { get; set; }
///C# 8.0 Feature: Default Implemented Methods
//internal void FunTwo ()
//{
// Console.WriteLine("Inside Interface");
//}
}
struct MyType : IMyType
{
public decimal Salary
{
get { return 0; }
set { }
}
public void FunOne()
{
Console.WriteLine("My Type Fun one");
}
}
}Example 3
namespace D04
{
struct Employee:IComparable
{
public int ID;
string Name;
public string GetName ()
{
return Name;
}
internal void SetName ( string name)
{
Name = name.Length <= 20 ? name : name.Substring(0, 20);
}
decimal salary;
public decimal Salary
{
get { return salary; }
internal set { salary = value >= 1200 ? value : 1200; }
}
public decimal Deductions
{
get { return 0.11M * salary; }
}
public Employee(int _id , string _Name , decimal _salary)
{
ID = _id;
Name = _Name;
salary = _salary;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return $"{ID}::{Name}::{salary}";
}
///return +ve this > obj
///return -ve this < obj
///return 0 this == obj
///items[j].compareTo(items[j+1]) //Inside Sort
public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
//foreach (var item in (new StackTrace()).GetFrames())
// Console.WriteLine(item.GetMethod().Name);
Employee Right = (Employee)obj; //UnBoxing
//if (salary > Right.salary)
// return 1;
//else if (salary < Right.salary)
// return -1;
//else
// return 0;
return salary.CompareTo(Right.salary);
}
}
class Program
{
static void MainV1(string[] args)
{
Employee[] EArr = new Employee[3]
{
new Employee(5 , "Ahmed Aly" , 17000),
new Employee(8 , "Sayed Aly" , 5000),
new Employee(2 , "Mona Aly" , 10000)
};
Array.Sort(EArr);
foreach (var item in EArr)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}