Commonly Used Data Types in SQL Server
| Data Type | Description | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| int | Integer, whole numbers | IDs, counts, primary keys |
| varchar(n) | Variable-length string | Names, descriptions |
| datetime | Date and time | Timestamp for records, events |
| decimal(p,s) | Fixed precision and scale numbers | Prices, exact financial calculations |
| bit | Integer that can be 0, 1, or NULL | Boolean-like flags |
| nvarchar(n) | Variable-width Unicode string | Multilingual text, product names |
| float | Floating-point number | Scientific calculations, measurements |
| money | Monetary data | Financial transactions, currency |
SQL Server Data Types
String Data Types
| Data Type | Description | Max Size | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| char(n) | Fixed-width character string | 8,000 characters | Defined width |
| varchar(n) | Variable-width character string | 8,000 characters | 2 bytes + chars |
| varchar(max) | Variable-width character string | 1,073,741,824 characters | 2 bytes + chars |
| text | Variable-width character string | 2GB of text data | 4 bytes + chars |
| nchar | Fixed-width Unicode string | 4,000 characters | Width x 2 |
| nvarchar(n) | Variable-width Unicode string | 4,000 characters | |
| nvarchar(max) | Variable-width Unicode string | 536,870,912 characters | |
| ntext | Variable-width Unicode string | 2GB of text data | |
| binary(n) | Fixed-width binary string | 8,000 bytes | |
| varbinary(n) | Variable-width binary string | 8,000 bytes | |
| varbinary(max) | Variable-width binary string | 2GB | |
| image | Variable-width binary data | 2GB |
الفرق بين الـ char, varchar: انت لو حددت انه هيخزن 50 حرف وبعدين مخزنتش غير 10 فالباقي هيفضلوا محجوزين ومكانهم فاضي في الـ char انما في الـ varchar بياخد اللي محتاجه بس
لو جيت بعد كدا أعدل فالـ char فالمكان كدا كدا محجوز انما في الـ varchar هيروح يشوفلي مكان فلو مش هغير كتير يبقا الأحسن varchar
جدول يوضح الفرق بين CHAR, VARCHAR, NCHAR, وNVARCHAR:
| النوع | الطول | يدعم Unicode | استهلاك المساحة | الاستخدامات |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHAR | ثابت | لا | طول النص المحدد مسبقًا | نصوص ثابتة (مثل أكواد الدول). |
| VARCHAR | متغير | لا | طول النص الفعلي + 1 بايت | نصوص متغيرة (مثل الأسماء). |
| NCHAR | ثابت | نعم | طول النص المحدد × 2 بايت | نصوص ثابتة بلغات متعددة. |
| NVARCHAR | متغير | نعم | طول النص الفعلي × 2 + 2 بايت | نصوص متغيرة بلغات متعددة. |
مثال سريع لكل نوع:
- الـCHAR(3): تخزين “EG ” (ثابت بـ 3 خانات).
- الـVARCHAR(50): تخزين “Ahmed” (يستهلك 6 بايت فقط).
- الـNCHAR(3): تخزين “عرب” (6 بايت).
- الـNVARCHAR(50): تخزين “محمد” (10 بايت).
Numeric Data Types
| Data Type | Description | Range | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| bit | Integer (0, 1, or NULL) | - | 1 bit |
| tinyint | Small integer | 0 to 255 | 1 byte |
| smallint | Small integer | -32,768 to 32,767 | 2 bytes |
| int | Standard integer | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | 4 bytes |
| bigint | Large integer | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 | 8 bytes |
| decimal(p,s) | Fixed precision and scale numbers (custom fractions) | -10^38 +1 to 10^38 –1 | 5-17 bytes |
| numeric(p,s) | Fixed precision and scale numbers (same as decimal) | -10^38 +1 to 10^38 –1 | 5-17 bytes |
| smallmoney | Small monetary data (4 fractions) | -214,748.3648 to 214,748.3647 | 4 bytes |
| money | Large monetary data (8 fractions) | -922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807 | 8 bytes |
| float(n) | Floating-point number (8 fractions) | -1.79E + 308 to 1.79E + 308 | 4 or 8 bytes |
| real | Smaller floating-point number (4 fractions) | -3.40E + 38 to 3.40E + 38 | 4 bytes |
Date and Time Data Types
| Data Type | Description | Storage |
|---|---|---|
| datetime | Date and time, accurate to 3.33 milliseconds | 8 bytes |
| datetime2 | Date and time, accurate to 100 nanoseconds | 6-8 bytes |
| smalldatetime | Date and time, accurate to 1 minute | 4 bytes |
| date | Date only | 3 bytes |
| time | Time only, accurate to 100 nanoseconds | 3-5 bytes |
| datetimeoffset | Date, time, and timezone offset | 8-10 bytes |
| timestamp | Unique number updated with each modification | - |
Other Data Types
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| sql_variant | Stores various data types, except text, ntext, and timestamp |
| uniqueidentifier | Stores a globally unique identifier (GUID) |
| xml | Stores XML-formatted data, up to 2GB |
| cursor | Stores a reference to a cursor for database operations |
| table | Stores a result set for later processing |
| Image | 2D binary array |
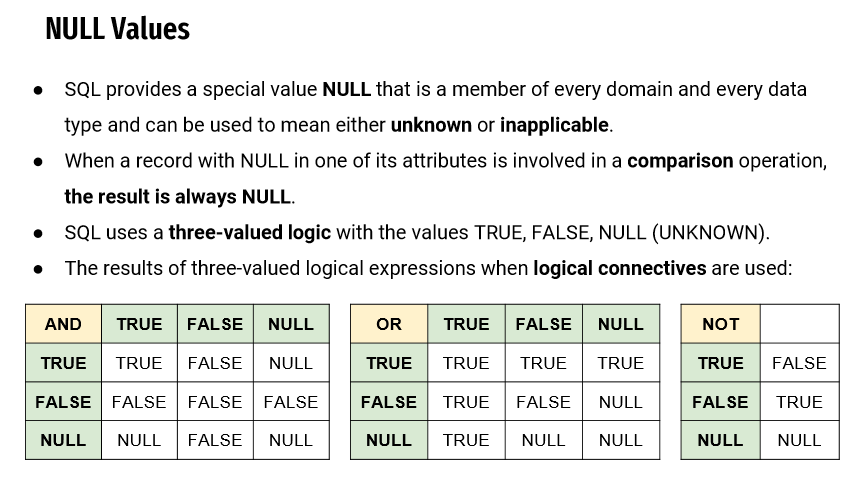
NULL Values
Differences Between SQL Server, MySQL, and MS Access Data Types
| Feature | SQL Server | MySQL | MS Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| String Types | Extensive Unicode support with nvarchar, variable and fixed-length types | Flexible string storage, including BLOB and TEXT types | Simpler options with limited Unicode support |
| Numeric Types | Detailed precision with decimal(p,s), money, float | Wide range with floating-point and exact types | Fewer options, suited for smaller datasets |
| Date and Time Precision | High precision options like datetime2 with 100 nanoseconds accuracy | Basic date and time with DATE, DATETIME | Limited options, with less precision for date/time |
| Binary and Large Object Types | Varied binary types (e.g., varbinary(max), image) | BLOB types with large size support | Basic BLOB support with OLE Object |
| Unique Identifiers | uniqueidentifier for globally unique IDs (GUIDs) | No direct equivalent, some GUID support through functions | AutoNumber for simple unique IDs |
| XML Support | XML data type for structured storage | Limited support for XML | No dedicated XML data type |
| Advanced Data Types | Types like sql_variant, cursor, and table for complex operations | Lacks these advanced SQL Server types | Simpler database, not suited for complex operations |