What is a JOIN in SQL?
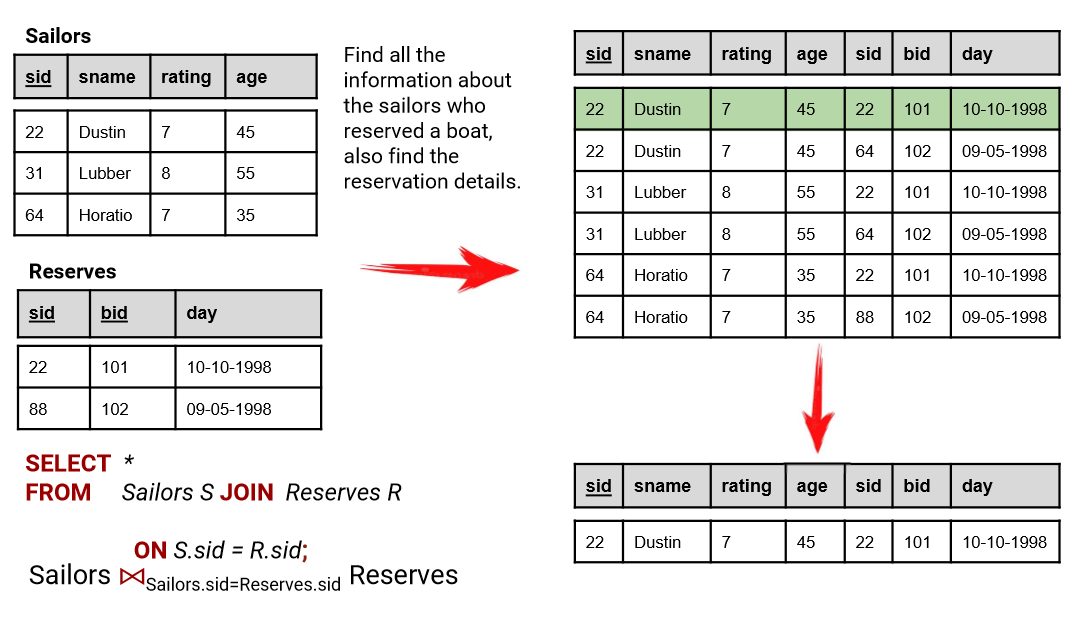
JOIN is a clause used in SQL to link data from one table to another table using one or more data column shared between two tables.
In other words, we combine data of the two existing tables into one. For example, table1 has data about x and y, table2 has data about y and z, so we join table1 and table2 to get a table3 with all data of x, y, and z.
JOIN = Cartesian Product + SELECT
بمعنى اني بعمل كل الإحتمالات بين كل جدول والجدول التاني (كل صف يبقا مع كل الصفوف في الجدول التاني) وبعدين بختار منه على أساس SELECT معينة (ON)
How important is JOIN in SQL?
For storing data, it’s not efficient to put everything into one table as it makes the table become heavier and lower its performance a lot. So it’s better to divide information into many different tables, faster storing, faster retrieving. But every now and then, you will need to select data from multiple tables, that’s where JOIN comes in handy.
Normally a JOIN has an ON condition and depending on the type of JOINs, it will return all the record from one table, or both, if there’s a match with the ON condition.
8 types of JOINs and how to use them
بس عندنا 5 هما الأساسيين: OUTER FULL, LEFT, RIGHT, INNER, CROSS
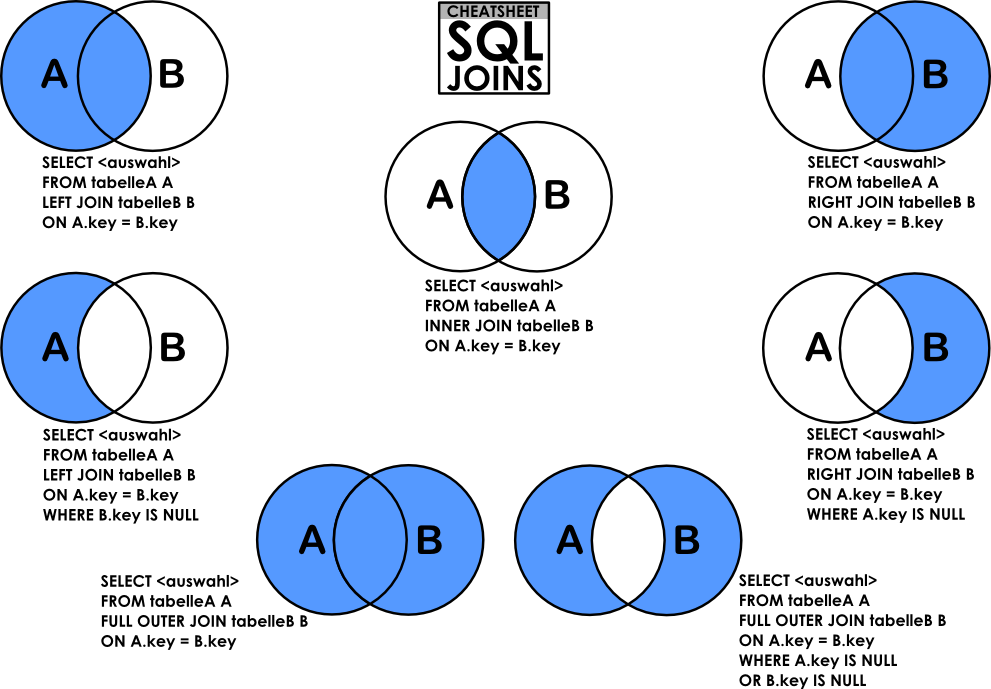

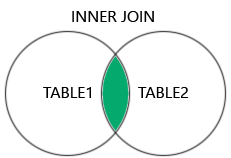
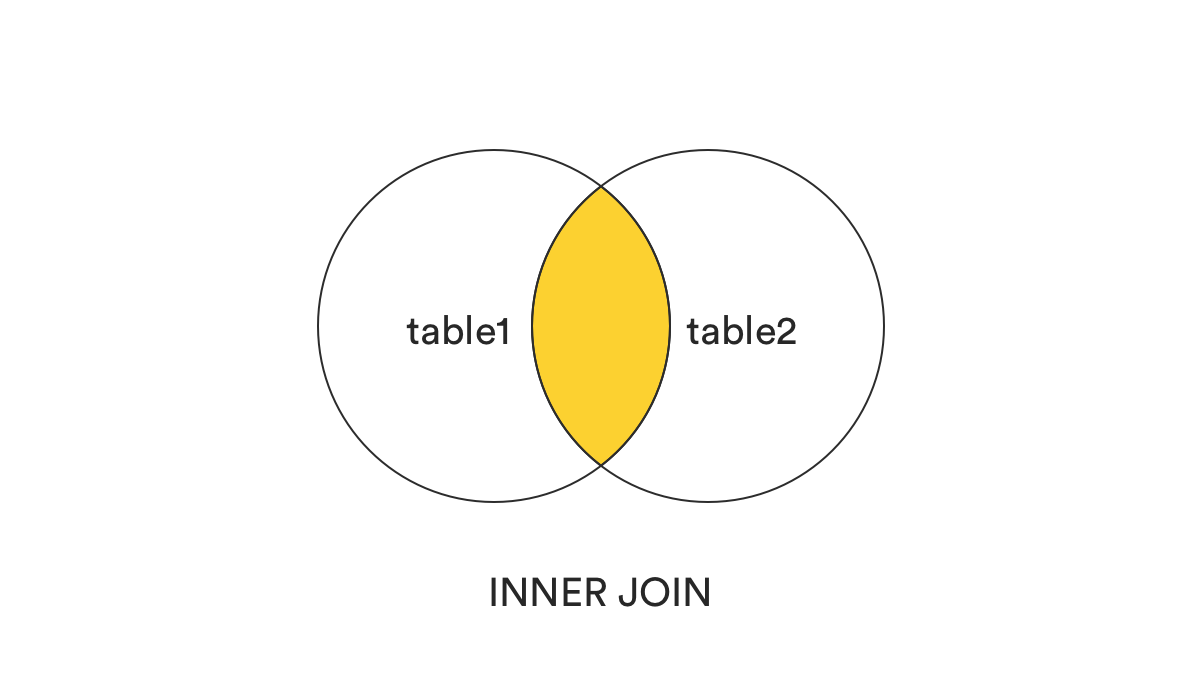
1. INNER JOIN (Default type)
- It’s the intersection between two tables.
- الـ Inner Join هو النوع الافتراضي في SQL، وده بيرجع النتائج اللي فيها تطابق بين الجداول في الـ Join. يعني لو في سجلات في جدول الموظفين مفيش ليها علاقة بقسم، مش هتظهر في النتائج.
SELECT *
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;ممكن من غير ما نكتب Inner عادي هي الـ Default
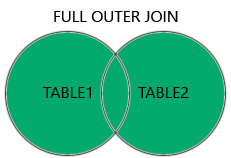
2. FULL (OUTER) JOIN
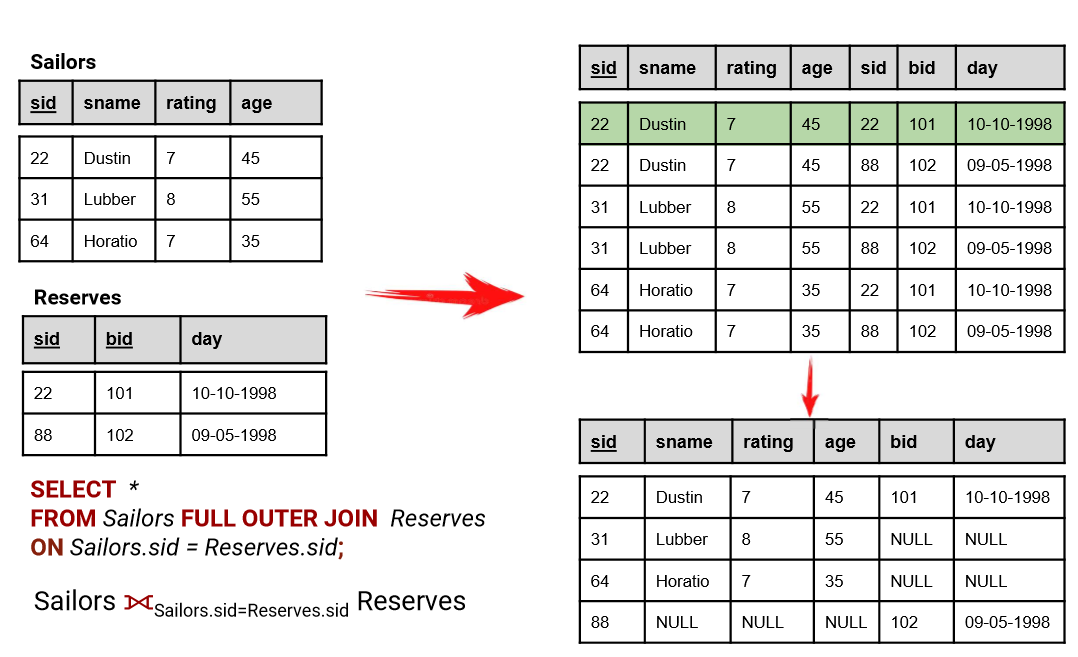
- returns all the records that match the ON condition, no matter which table they are stored in
- بيرجع كل البيانات من الجدولين. لو فيه علاقة بين السجلات، هيتجمعوا، ولو مفيش هيرجعوا مع قيم NULL.
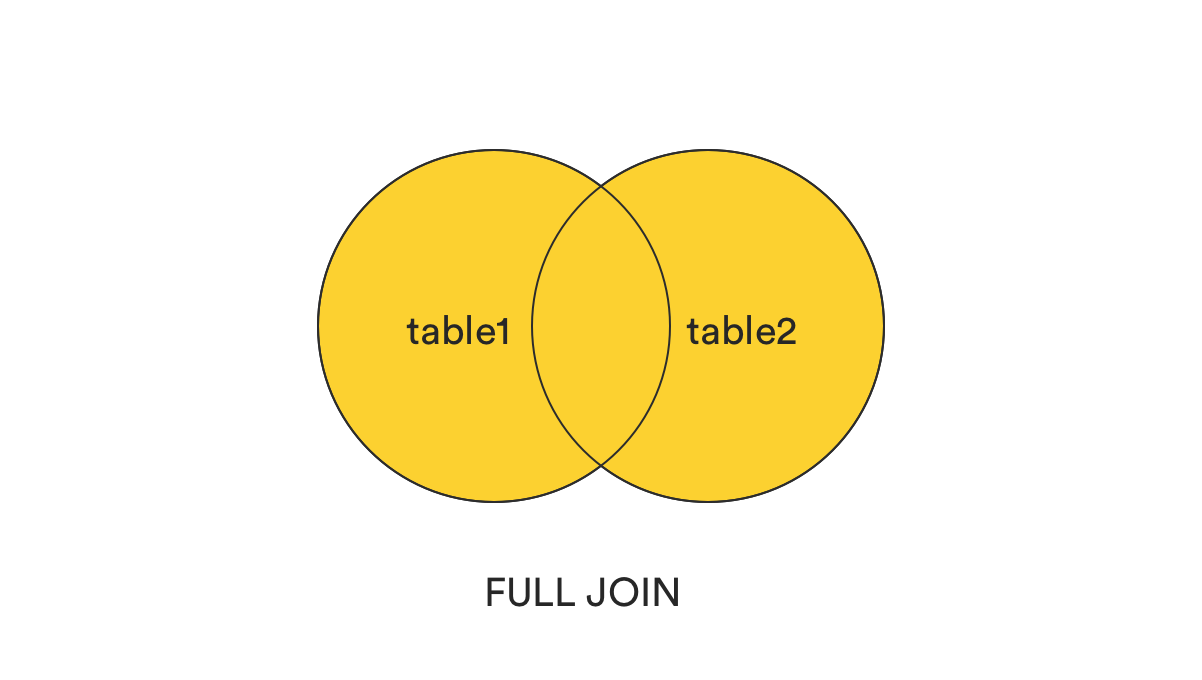
SELECT *
FROM table1
FULL JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;3. FULL (OUTER) JOIN without the intersection.
-
This clause returns all records that match the ON condition, excluding those are in common between two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
-
In plain term, it can be understood as (OUTER JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
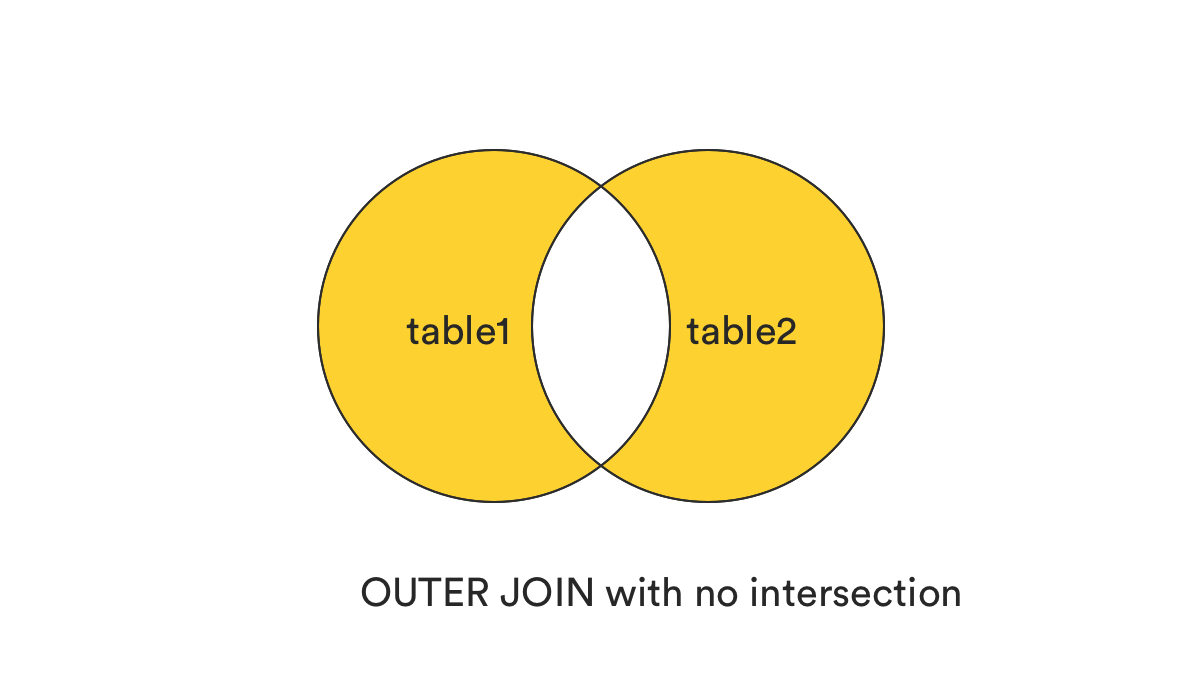
SELECT *
FROM table1 AS t1
FULL JOIN table2 AS t2
ON t1.col1 = t2.col2
WHERE t1.col1 IS NULL
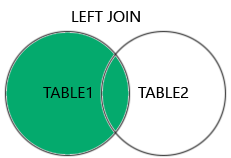
OR t1.col2 IS NULL;4. LEFT (OUTER) JOIN
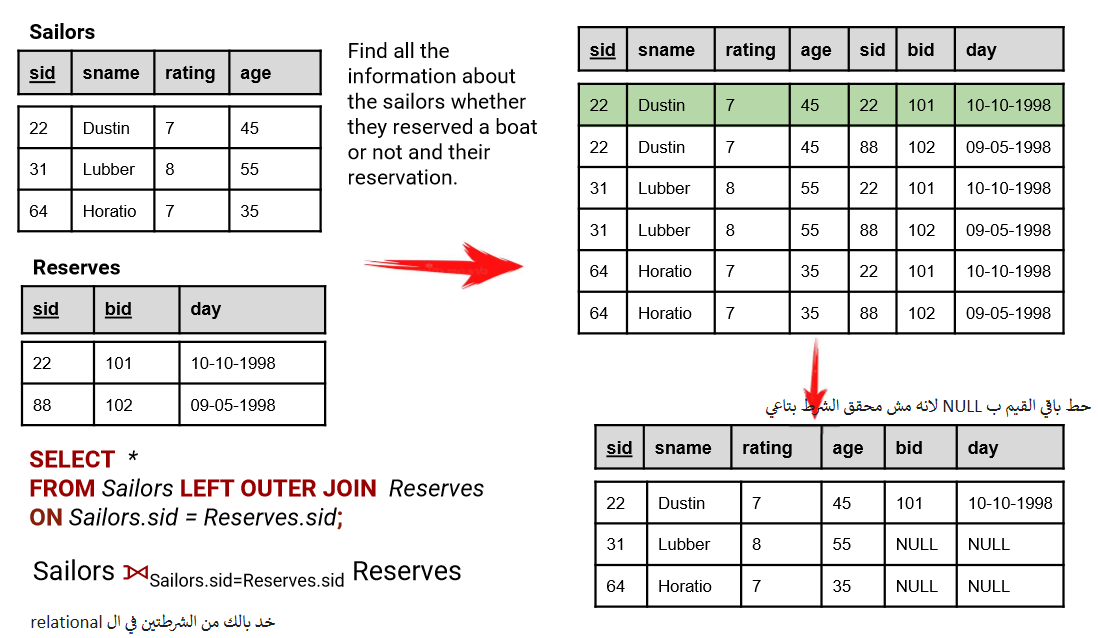
LEFT JOINreturns all records from the left table (table1) that matched the ON condition.- الـ Left Outer Join بيجمع البيانات من الجداول زي الـ Inner Join، لكن الفرق إنه هيشمل كل البيانات من الجدول اللي على الشمال (الـ Left Table) حتى لو مفيش علاقة مع الجدول اللي على اليمين.
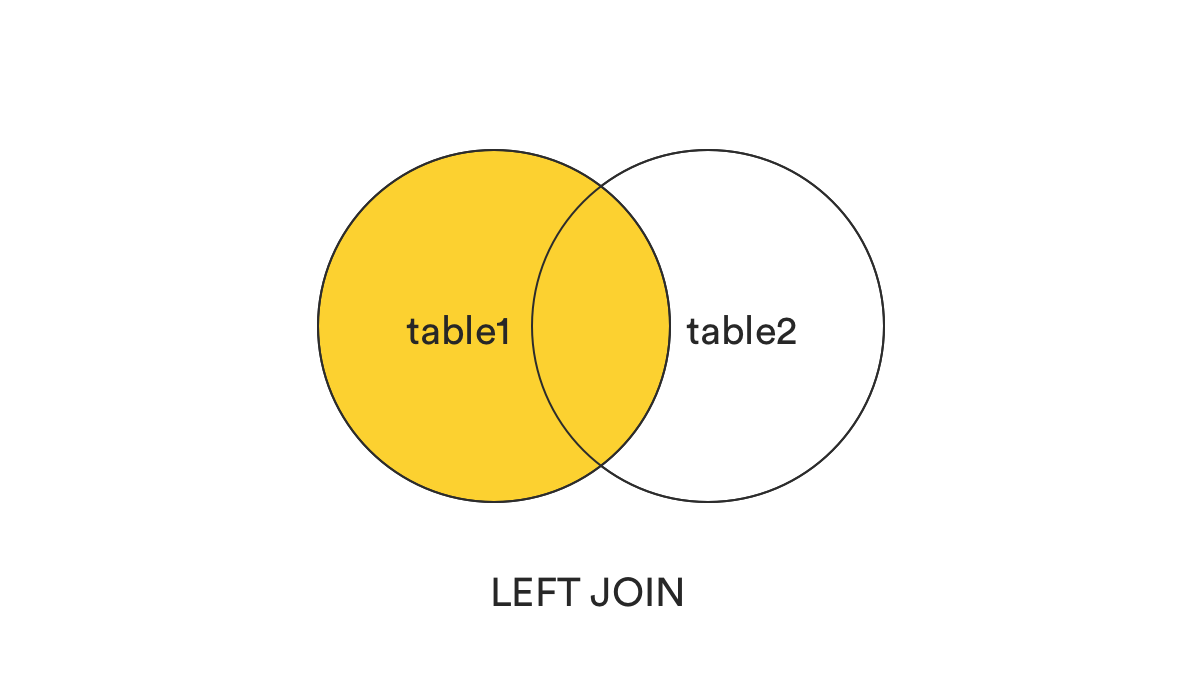
SELECT *
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;5. LEFT (OUTER) JOIN without the intersection
-
This clause returns all records from the left table (table1) that matched the ON condition, but exclude those are in common better two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
-
In plain term, it can be understood as (LEFT JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
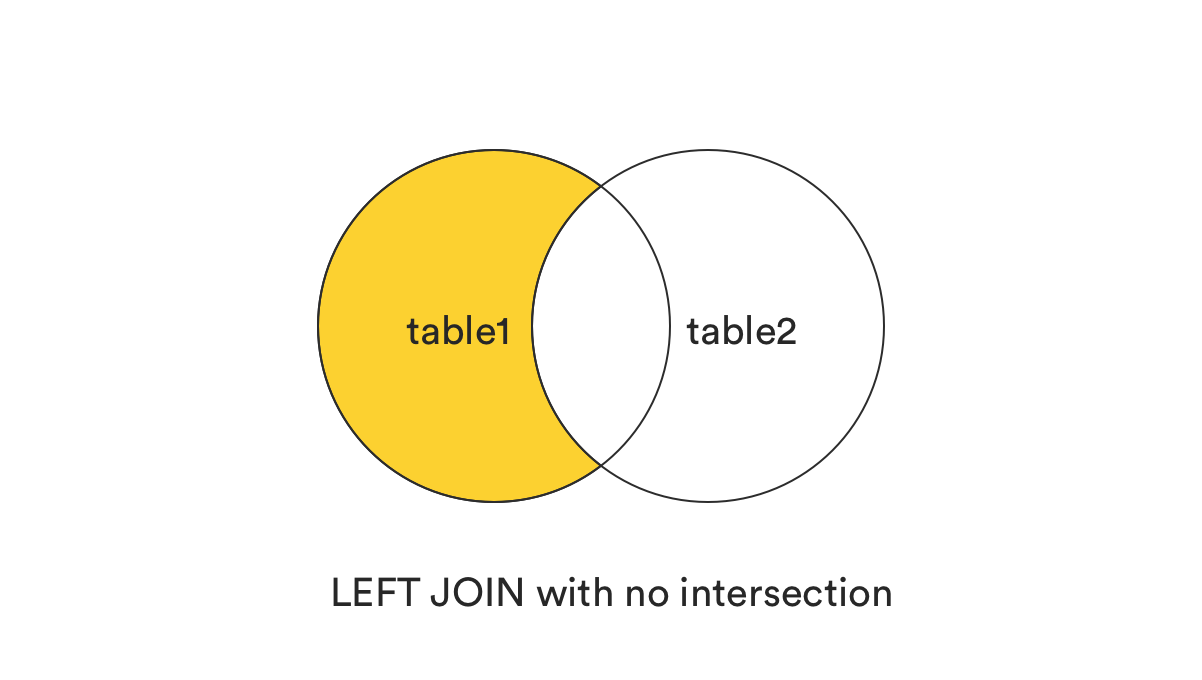
SELECT *
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2
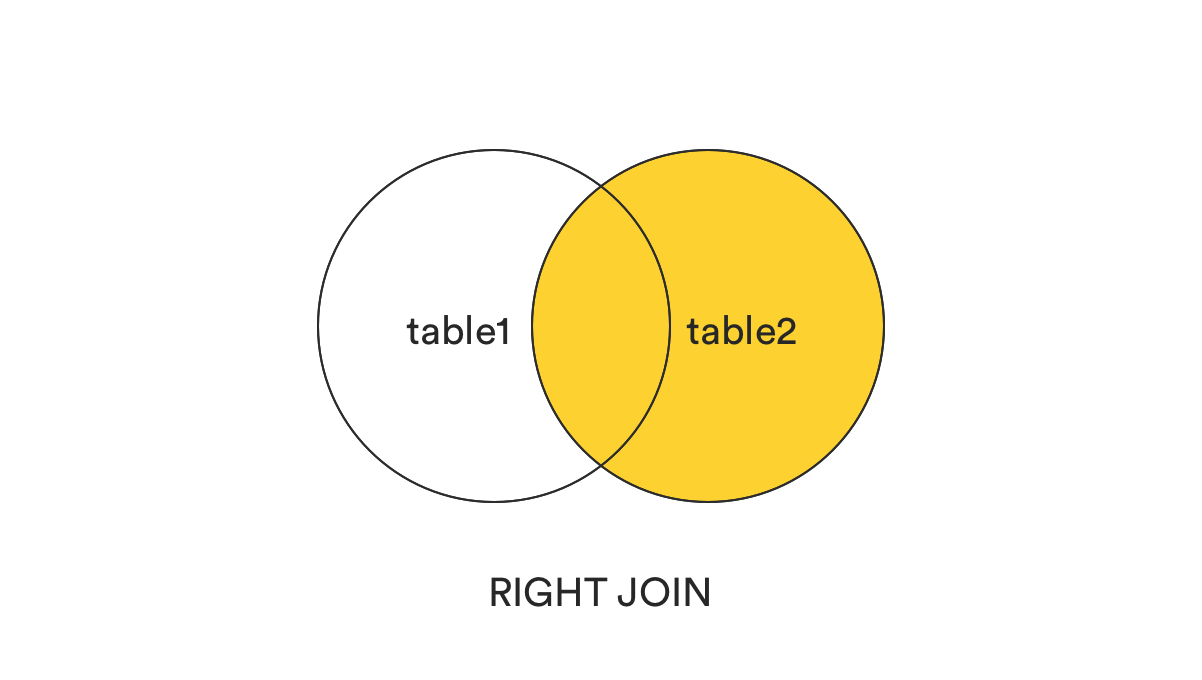
WHERE table2.col2 IS NULL;6. RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN
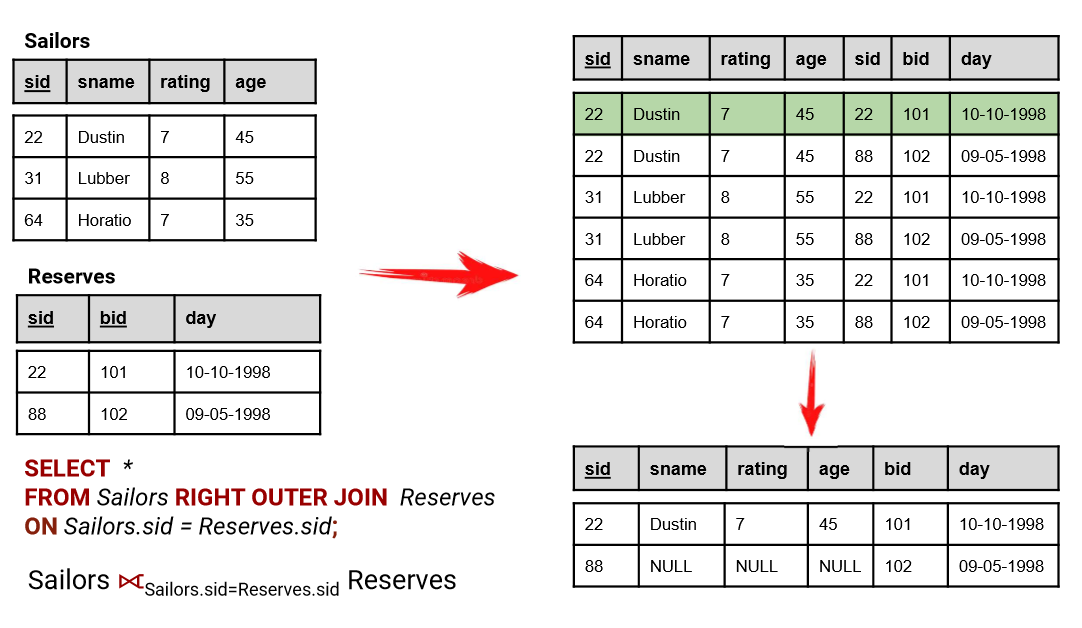
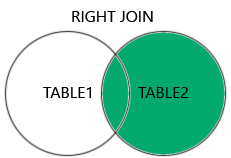
- In the opposite of
LEFT JOIN,RIGHT JOINreturns all records from the right table (table2) that matched the ON condition. - الـ Right Outer Join بيعمل نفس فكرة الـ Left Join بس بينفذها على الجدول اللي على اليمين (الـ Right Table). يعني هيرجع كل البيانات من جدول الأقسام حتى لو مفيش موظفين ليهم.
SELECT *
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;7. RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN without the intersection
-
This clause returns all records from the right table (table2) that matched the ON condition, but exclude those are in common better two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
-
In plain term, it can be understood as (RIGHT JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
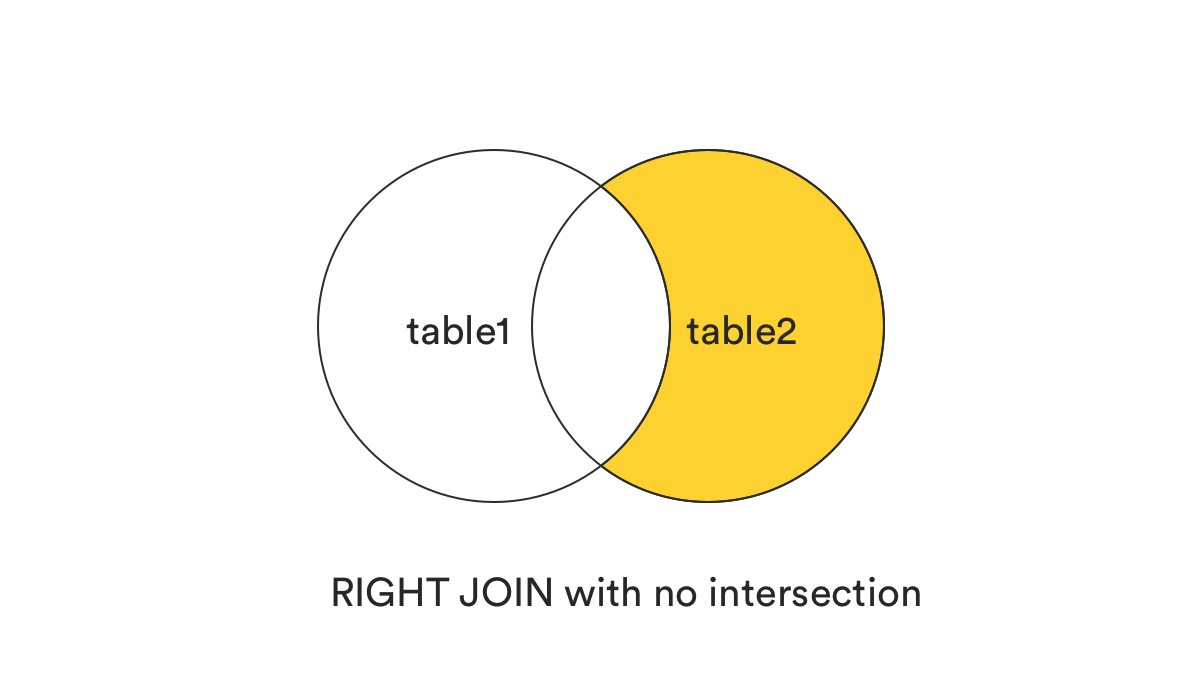
SELECT *
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2
WHERE table1.col1 IS NULL;8. Cross Join (Cartesian Join):
الـ Cross Join بيجمع كل صف من الجدول الأول مع كل صف من الجدول التاني. يعني هيرجع كل الاحتمالات الممكنة من دمج البيانات بين الجداول.
SELECT * FROM table_A, table_B;
-- CROSS
SELECT *
FROM table_A AS A
CROSS JOIN table_B AS Bالنتيجة هتكون كل تركيبة ممكنة من الصفوف بين الجدولين.
أنواع تانية من الـ Joins:
فيه كمان أنواع تانية زي الـ Self Join وNatural Join، اللي بيتنفذوا باستخدام الـ JOIN وUNION مع بعض.
Natural Join:
الـ Natural Join هو نوع من الـ JOIN بيجمع بين جدولين استنادًا إلى الأعمدة اللي ليهم نفس الاسم في الجدولين. الـ Natural Join بيعمل الربط بشكل تلقائي باستخدام الأعمدة المشتركة بينهم، وبيحذف الأعمدة المتكررة في النتيجة.
مثال:
لو عندك جدولين:
employees(employee_id, department_id, name)departments(department_id, department_name)
واستخدمت الاستعلام ده:
SELECT * FROM employees NATURAL JOIN departments;الـ Natural Join هيربط الجدولين باستخدام department_id (لأن ده العمود المشترك بين الجدولين) وهيرجع كل البيانات مع حذف العمود المتكرر.
Self Join:
الـ Self Join هو نوع من الـ JOIN بيتم فيه ربط الجدول بنفسه. ده بيبقى مفيد لو عايز تشوف علاقات بين البيانات داخل نفس الجدول. في الـ Self Join، بنستخدم alias علشان نفرق بين الجدولين اللي بنستخدمهم رغم إنهم نفس الجدول.
مثال:
لو عندك جدول employees وفيه عمود manager_id بيحدد مين المدير بتاع الموظف، وعايز تجيب بيانات الموظفين مع بيانات مديريهم:
SELECT e.name AS employee_name, m.name AS manager_name
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id;في المثال ده، employees اتعاملت مع نفسها عن طريق استخدام alias (هوا e للموظف و m للمدير).
استخدام ON
الهدف الأساسي من ON هو تحديد العلاقة بين الجدولين، لكن فيه أكتر من طريقة أو ظروف ممكن تتغير فيها الكتابة:
1. استخدام شروط متعددة داخل ON:
لو العلاقة بين الجدولين معقدة أكتر وبتعتمد على أكتر من عمود مشترك، ممكن تضيف أكتر من شرط باستخدام AND أو OR.
SELECT E.Name, D.DepartmentName
FROM Employees AS E
INNER JOIN Departments AS D
ON E.DepartmentID = D.DepartmentID AND E.Status = D.Status;2. استخدام أسماء مختلفة للأعمدة:
لو الأعمدة المشتركة ليها أسماء مختلفة في الجدولين، برضو لازم تستخدم ON بس بتمشي بنفس الفكرة.
SELECT E.Name, D.DepartmentName
FROM Employees AS E
INNER JOIN Departments AS D
ON E.Dept_ID = D.ID;3. الاعتماد على USING بدلًا من ON:
لو العمود المشترك له نفس الاسم في الجدولين، وبعض قواعد البيانات زي MySQL و PostgreSQL بتدعم استخدام USING كطريقة مختصرة.
SELECT E.Name, D.DepartmentName
FROM Employees AS E
INNER JOIN Departments AS D
USING (DepartmentID);4. استخدام شروط داخل WHERE بدلًا من ON:
في حالات معينة، ممكن تكتب العلاقة داخل WHERE بدلًا من ON، لكن ده مش مستحب لأنه أقل وضوحًا وأصعب في الصيانة.
SELECT E.Name, D.DepartmentName
FROM Employees AS E, Departments AS D
WHERE E.DepartmentID = D.DepartmentID;ملاحظة:
دي طريقة قديمة ومش مستحبة مقارنة باستخدام الـ JOIN الصريح.
الأفضلية:
- الطريقة بـ
ONأوUSINGهي الأفضل والأكثر وضوحًا. - استخدم الشروط اللي تناسب العلاقة بين الجدولين حسب احتياجاتك.
الخلاصة
Here are the different types of the JOINs in SQL:
(INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tablesLEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right tableRIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left tableFULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table