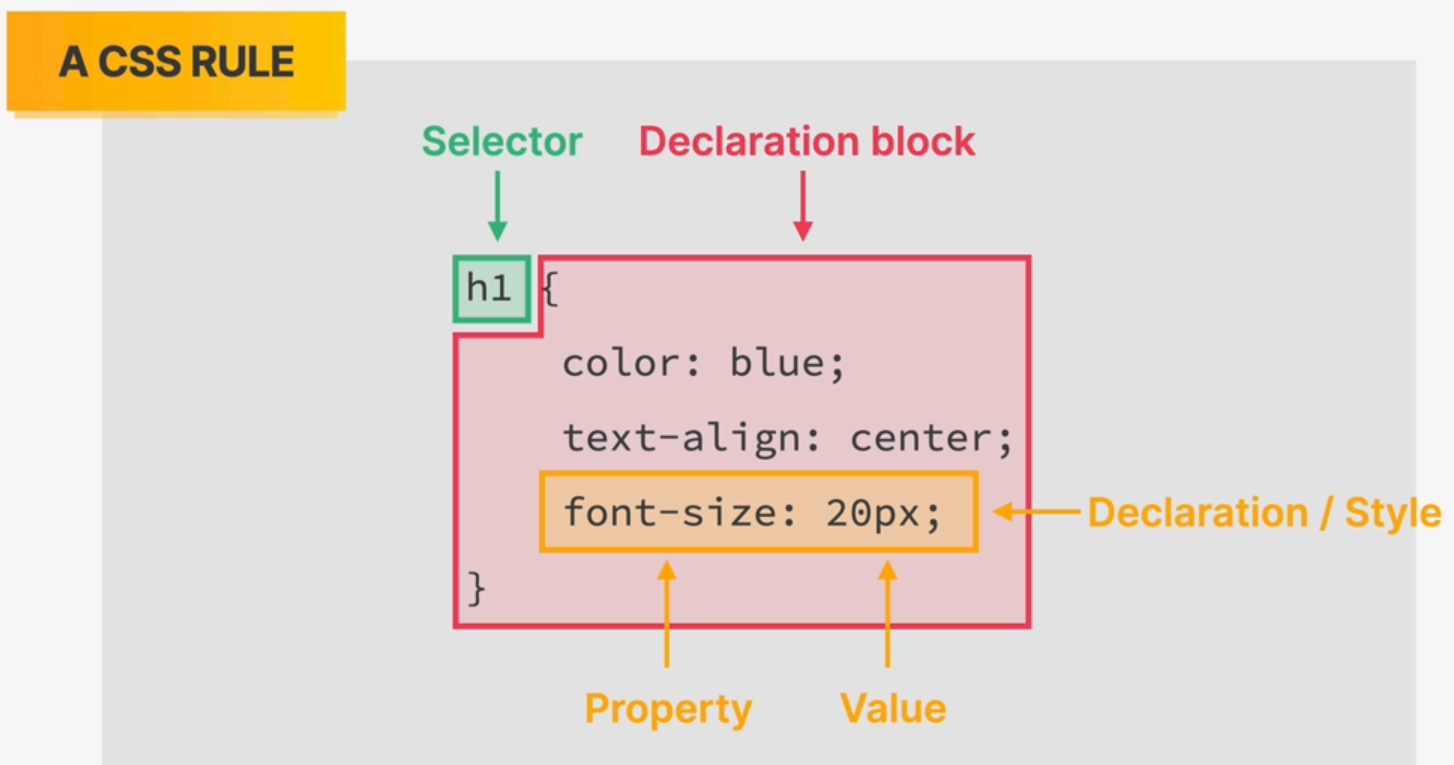
Selectors
- A selector designates exactly which element or elements within our HTML to target and apply styles (such as color, size, and position) to.
- Selectors may include a combination of different qualifiers to select unique elements, all depending on how specific we wish to be.
- Selectors generally target an attribute value, such as an
idorclassvalue, or target the type of element, such as<h1>or<p>. - Within CSS, selectors are followed with curly brackets,
{}, which encompass the styles to be applied to the selected element. The selector here is targeting all<p>elements.
p { ... }Common Selectors Overview
| Example | Classification | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
h1 | Type Selector | Selects an element by its type |
.tagline | Class Selector | Selects an element by the class attribute value, which may be reused multiple times per page |
#intro | ID Selector | Selects an element by the ID attribute value, which is unique and to only be used once per page |
Universal selector
Selects all HTML elements on the page.
* {
text-align: center;
color: blue;
}Properties
- Property determines the styles that will be applied to that element.
- Property names fall after a selector, within the curly brackets,
{}, and immediately preceding a colon,:. - There are numerous properties we can use, such as
background,color,font-size,height, andwidth, and new properties are often added.
p {
color: ...;
font-size: ...;
}Values
Values can be identified as the text between the colon, :, and semicolon, ;.
p {
color: orange;
font-size: 16px;
}